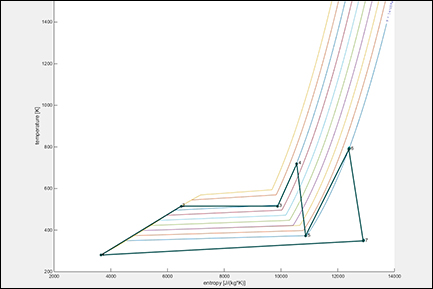
Tutorial | Forced Circulation Boiler
In this tutorial we’d like to show how easy it is to create complex dynamic models with Thermolib. Therefore, we choose a gas fired forced circulation boiler with air preheater and economizer.
In the beginning of the development, when there is only a rather rough idea of the process in the mind of the designer, a steady state model comes in handy.
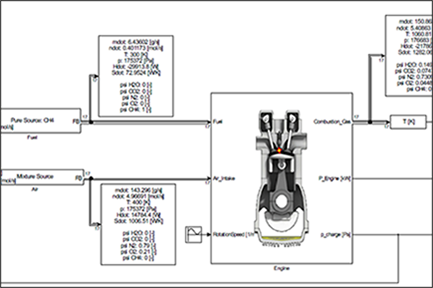
Tutorial | Modeling a Gas Engine
The importance of self-sustaining energy supplies increases more and more. Therefore, it is common practice to combine a conventional engine with a battery and or reuse waste heat. This example will show how to model a gas engine with Thermolib. So, what’s the fuss? At a top level the engine is not a steady-state process and takes place in a closed volume. This bears some pitfalls, which we aim to tackle.
Webinar | What’s New in Release 5.3?
Please accept YouTube cookies to play this video. By accepting you will be accessing content from YouTube, a service provided by an external third party.
If you accept this notice, your choice will be saved and the page will refresh.
This webinar demonstrates the most important improvements, including the Species Data Import Module for importing thermophysical species data from Refprop, NIST webbook etc. We will also demonstrate the easy use of command line functions within MATLAB.
Tutorial | Running a demo model
Please accept YouTube cookies to play this video. By accepting you will be accessing content from YouTube, a service provided by an external third party.
If you accept this notice, your choice will be saved and the page will refresh.
Presentation | Plants Going Green: Intelligent Optimization for Power Plants Part 1 to 3
Please accept YouTube cookies to play this video. By accepting you will be accessing content from YouTube, a service provided by an external third party.
If you accept this notice, your choice will be saved and the page will refresh.
MathWorks Energy and Utilities Virtual Conference — Sept. 20, 2012
Using model-predictive control, the intelligent optimizer reduces emissions and cuts costs all while improving combustion efficiency. We demonstrate the end-to-end optimization solution, developed with a model-based approach, and more importantly, we present the tangible results from a large-scale power plant. The results underline the environmental and financial gains that paid off the system within a year. The solution devised is modular, highly customizable and robust.
Presentation | Modeling Thermodynamics in Simulink Part 1 to 3
Please accept YouTube cookies to play this video. By accepting you will be accessing content from YouTube, a service provided by an external third party.
If you accept this notice, your choice will be saved and the page will refresh.
- Absorption Heat Pump
- Combined Cycle Power Plant
- Solar Thermal Plant
- Solar Thermal Plant
- Fuel Cell Vehicle
- Air Conditioning
- Reforming Process
In addition, special featues like thermodynamic balancing and command-line functions are further explained. Wrapping up the presentation, the summary repeats the key features of thermodynamic modeling with Thermolib.
Webinar | Modeling Hydraulic Networks in Heating and Cooling Cycles Part 1 to 4
Please accept YouTube cookies to play this video. By accepting you will be accessing content from YouTube, a service provided by an external third party.
If you accept this notice, your choice will be saved and the page will refresh.
In building such networks, use of pressure feedback in the network is necessary. Thermolib offers solutions to deal with this in Simulink, and we’ll go over those solutions in this webinar.
Webinar | What’s New in Release 5.2
Please accept YouTube cookies to play this video. By accepting you will be accessing content from YouTube, a service provided by an external third party.
If you accept this notice, your choice will be saved and the page will refresh.
- Unified and flexible parameterizable hydraulic components to make selection of blocks more user-friendly.
- A new method, the volume-flow-volume approach, is now part of the Thermolib repertoire to simulate hydraulic systems.
- Improved density calculations for two phase region of mixture fluids. Results of simulations in the two-phase-region are significantly more accurate.
- Many more.
We will especially highlight the new unified approach for the hydraulic components and for one_half_lastmodeling using the “volume-flow-volume” method.